Convierta la imagen RGB al espacio de color Lab (por ejemplo, cualquier espacio de color con un canal de luminancia funcionará bien), luego aplique la ecualización de histograma adaptable al canal L. Finalmente, convierta el Lab resultante de nuevo a RGB.
Lo que desea es el algoritmo CLAHE (Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization) de OpenCV. Sin embargo, que yo sepa, no está documentado. Hay un ejemplo en python. Puede leer sobre CLAHE en Graphics Gems IV, pp474-485
He aquí un ejemplo de CLAHE en acción: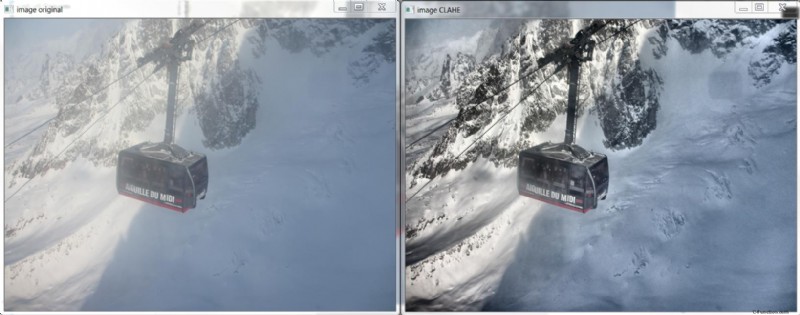
Y aquí está el C++ que produjo la imagen de arriba, basado en http://answers.opencv.org/question/12024/use-of-clahe/, pero extendido para color.
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <vector> // std::vector
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// READ RGB color image and convert it to Lab
cv::Mat bgr_image = cv::imread("image.png");
cv::Mat lab_image;
cv::cvtColor(bgr_image, lab_image, CV_BGR2Lab);
// Extract the L channel
std::vector<cv::Mat> lab_planes(3);
cv::split(lab_image, lab_planes); // now we have the L image in lab_planes[0]
// apply the CLAHE algorithm to the L channel
cv::Ptr<cv::CLAHE> clahe = cv::createCLAHE();
clahe->setClipLimit(4);
cv::Mat dst;
clahe->apply(lab_planes[0], dst);
// Merge the the color planes back into an Lab image
dst.copyTo(lab_planes[0]);
cv::merge(lab_planes, lab_image);
// convert back to RGB
cv::Mat image_clahe;
cv::cvtColor(lab_image, image_clahe, CV_Lab2BGR);
// display the results (you might also want to see lab_planes[0] before and after).
cv::imshow("image original", bgr_image);
cv::imshow("image CLAHE", image_clahe);
cv::waitKey();
}
La respuesta proporcionada por Bull es la mejor que he encontrado hasta ahora. Lo he estado usando para. Aquí está el código de python para lo mismo:
import cv2
#-----Reading the image-----------------------------------------------------
img = cv2.imread('Dog.jpg', 1)
cv2.imshow("img",img)
#-----Converting image to LAB Color model-----------------------------------
lab= cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB)
cv2.imshow("lab",lab)
#-----Splitting the LAB image to different channels-------------------------
l, a, b = cv2.split(lab)
cv2.imshow('l_channel', l)
cv2.imshow('a_channel', a)
cv2.imshow('b_channel', b)
#-----Applying CLAHE to L-channel-------------------------------------------
clahe = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=3.0, tileGridSize=(8,8))
cl = clahe.apply(l)
cv2.imshow('CLAHE output', cl)
#-----Merge the CLAHE enhanced L-channel with the a and b channel-----------
limg = cv2.merge((cl,a,b))
cv2.imshow('limg', limg)
#-----Converting image from LAB Color model to RGB model--------------------
final = cv2.cvtColor(limg, cv2.COLOR_LAB2BGR)
cv2.imshow('final', final)
#_____END_____#
Basado en el gran ejemplo de C++ escrito por Bull, pude escribir este método para Android.
He sustituido "Core.extractChannel" por "Core.split". Esto evita un problema conocido de pérdida de memoria.
public void applyCLAHE(Mat srcArry, Mat dstArry) {
//Function that applies the CLAHE algorithm to "dstArry".
if (srcArry.channels() >= 3) {
// READ RGB color image and convert it to Lab
Mat channel = new Mat();
Imgproc.cvtColor(srcArry, dstArry, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2Lab);
// Extract the L channel
Core.extractChannel(dstArry, channel, 0);
// apply the CLAHE algorithm to the L channel
CLAHE clahe = Imgproc.createCLAHE();
clahe.setClipLimit(4);
clahe.apply(channel, channel);
// Merge the the color planes back into an Lab image
Core.insertChannel(channel, dstArry, 0);
// convert back to RGB
Imgproc.cvtColor(dstArry, dstArry, Imgproc.COLOR_Lab2BGR);
// Temporary Mat not reused, so release from memory.
channel.release();
}
}
Y llámalo así:
public Mat onCameraFrame(CvCameraViewFrame inputFrame){
Mat col = inputFrame.rgba();
applyCLAHE(col, col);//Apply the CLAHE algorithm to input color image.
return col;
}